How does a blockchain transaction work?
by Scott Dutfield · 05/03/2019

The process behind a transfer is more complex than it might appear
The request ➡️
A user in the blockchain requests a transaction to be made.
Mining machine ➡️
Some of the machines on the network might be ‘mining’ machines and can, therefore, work on the transaction to earn cryptocurrency.
The network ➡️
The request is sent out to a peer-to-peer network of computers. Each computer is known as a ‘node’.
Validation ➡️
When the network nodes have checked the user’s status they’ll validate the transaction.
Verification ➡️
A verified transaction can involve all kinds of data, from cryptocurrency like Bitcoin to contracts or other important information.
Transaction complete ➡️
All of this happens in a few seconds. Moments later, the original user is notified that the transaction is complete.
In the chain ➡️
The block is added to the rest of the chain in a permanent form that can’t be edited.
The header ➡️
The new block contains a ‘header’, which is a small piece of information from the previous block in the chain.
Create a block!
The information that is being transferred is combined with the verification information to create a new block of data.
Hey big sender!
Could blockchain make the world go round?
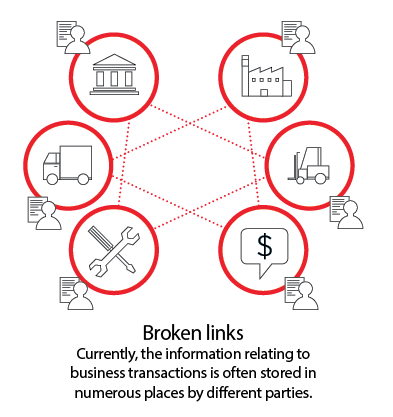
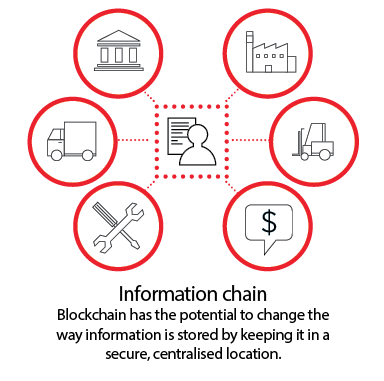
The pros of blockchain
👍Secure transfers: It’s a safe and confidential way to transfer data that can’t be edited.
👍Irreversible transactions: Transfers are safer because a buyer can’t take information then claim back the money.
👍The potential: Blockchain technology could make it easier for us to pay for things, access our medical records and even vote.
👍Cryptocurrencies can’t be frozen: If there’s a financial crisis, banks often freeze bank accounts. That can’t happen with cryptocurrencies.
The cons of blockchain
👎Hacks still happen: Some system hacks can still cause major problems, such as an attack that blocks a node from accessing the network.
👎Irreversible transactions!: When mistakes are made it can be more difficult to organise refunds or redistribution.
👎No regulators: Because Bitcoin is digital it has no official regulator. If the creator decided to split it, or change it, it could have major effects.
👎New tech can scare people: People don’t really understand blockchain or cryptocurrency, so making them mainstream will be
This article was originally published in How It Works issue 117, written by Stephen Ashby
For more science and technology articles, pick up the latest copy of How It Works from all good retailers or from our website now. If you have a tablet or smartphone, you can also download the digital version onto your iOS or Android device. To make sure you never miss an issue of How It Works magazine, subscribe today!





