How do astronomical clocks keep time?
by Scott Dutfield · 02/10/2019

How did these ancient timekeeping instruments work?
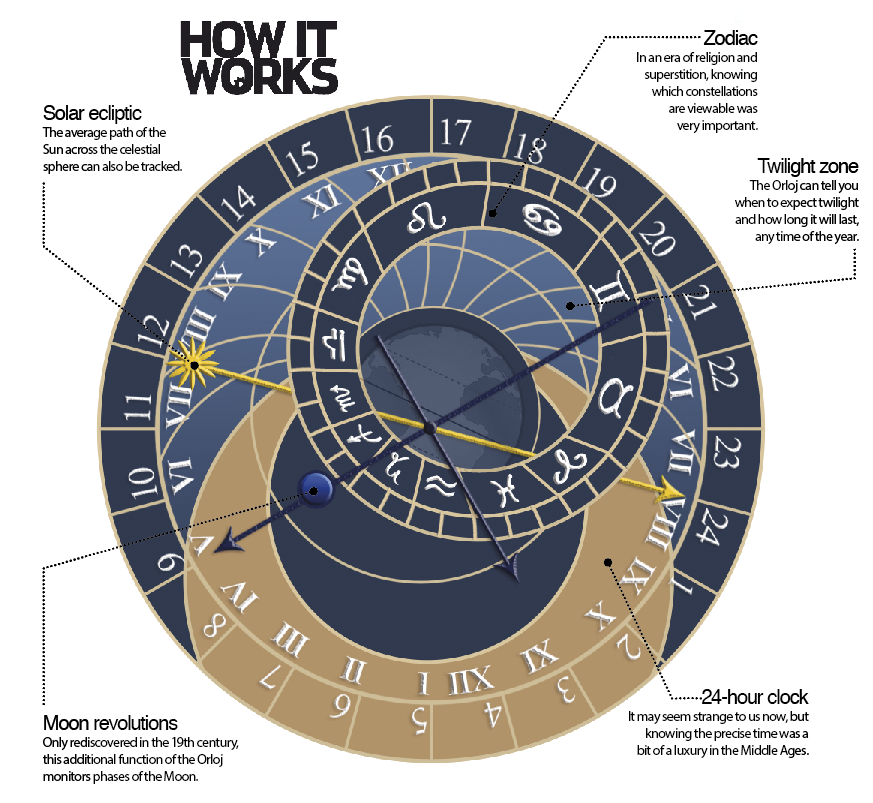
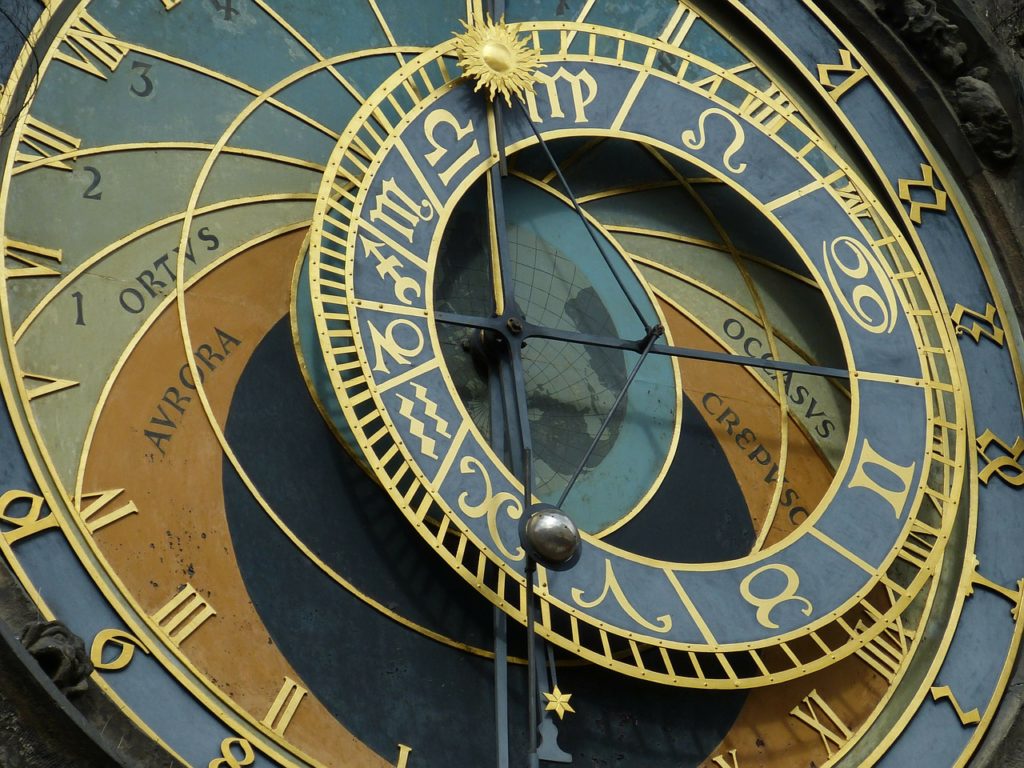
Astronomical clocks are timekeeping devices in the traditional sense. They were first used to calculate the position of the Moon, Sun and the stars in Ancient Greece, around the 2nd century BCE. The Middle Ages saw the popularity of clocks grow greatly and this included those that timed zodiacal events using crude mechanical techniques. In fact, they often required a much simpler (yet more reliable) sundial to readjust their timings.
Originally these clocks had no dials and simply struck at one-hour intervals, indicating the passing of time via the medium of sound. A 24-hour dial was later added for the convenience of the timekeeper, followed by a Sun clock that charted the position of the Sun across the sky. A Moon plate followed this, which worked in the same way but moved more slowly across the dial until it coincided with the Sun once again, 29 and a half days later, indicating a new Moon.
The astronomical clock was then given 12 zodiac signs through which the Sun passed over the course of the year, though during a leap year the clock was usually stopped for a day to avoid timing problems in the future.
An instrument for measuring celestial bodies, called an astrolabe, could also be added to chart the position of the zodiac signs throughout the year. This was useful as winter signs (eg Capricorn) spend less time visible above the horizon than summer signs (eg Gemini).
Interest in astronomical clocks saw a resurgence in the mid- to late-17th century as astronomy became en vogue in the wake of Galileo’s major influence on the scientific community. These clocks were used frequently right up to the 19th century, with religion playing a key role in their design. They were particularly popular in Islamic countries, where an astrolabe could be used to calculate the regular prayer times.
How the Orloj measures time
This article was originally published in How It Works issue 37, written by Ben Biggs
For more science and technology articles, pick up the latest copy of How It Works from all good retailers or from our website now. If you have a tablet or smartphone, you can also download the digital version onto your iOS or Android device. To make sure you never miss an issue of How It Works magazine, subscribe today!